Describe Bohr’s model of the atom.
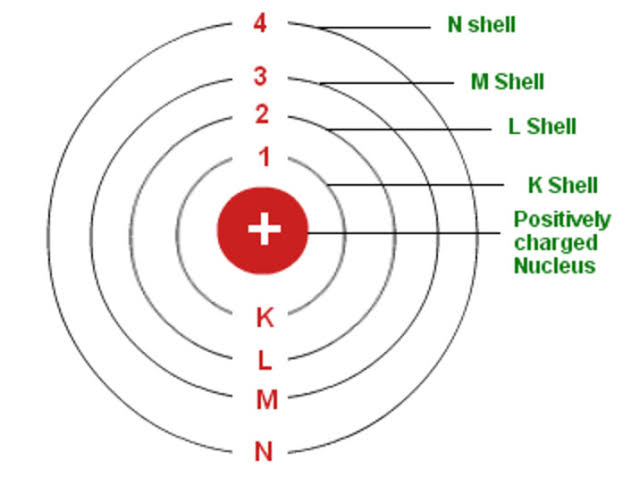
Bohr’s model of the atom, proposed in 1913, is a model that attempts to explain the structure of the atom and how electrons behave within it. The model postulates that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific, quantized energy levels (or shells) rather than in any arbitrary path. These orbits are not random but have distinct energy values.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
1. Nucleus:
The atom has a positively charged nucleus at its center, containing protons and neutrons.
2. Electrons in Orbits:
Electrons, which are negatively charged, orbit the nucleus in specific, circular paths called orbits or shells.
3. Quantized Energy Levels:
Each orbit has a specific, fixed energy level. Electrons can only exist in these specific orbits, not between them.
4. Energy Transitions:
When an electron moves from one orbit to another, it either absorbs or emits energy in the form of a photon.
5. Ground State and Excited State:
When an electron is in the lowest energy level (closest to the nucleus), it’s in the ground state. If it absorbs energy and moves to a higher energy level, it’s in an excited state.
6. No Energy Radiation in Orbits:
Electrons in these orbits do not radiate energy, a concept that contradicts classical physics.
7. Quantization:
Bohr’s model introduced the concept of quantization, meaning that energy and other physical properties, like electron orbits, are not continuous but exist in discrete, specific values.
Bohr’s model was a significant step in understanding atomic structure and was a crucial foundation for later development of quantum mechanics. However, it had limitations and was later refined by more advanced models of the atom.