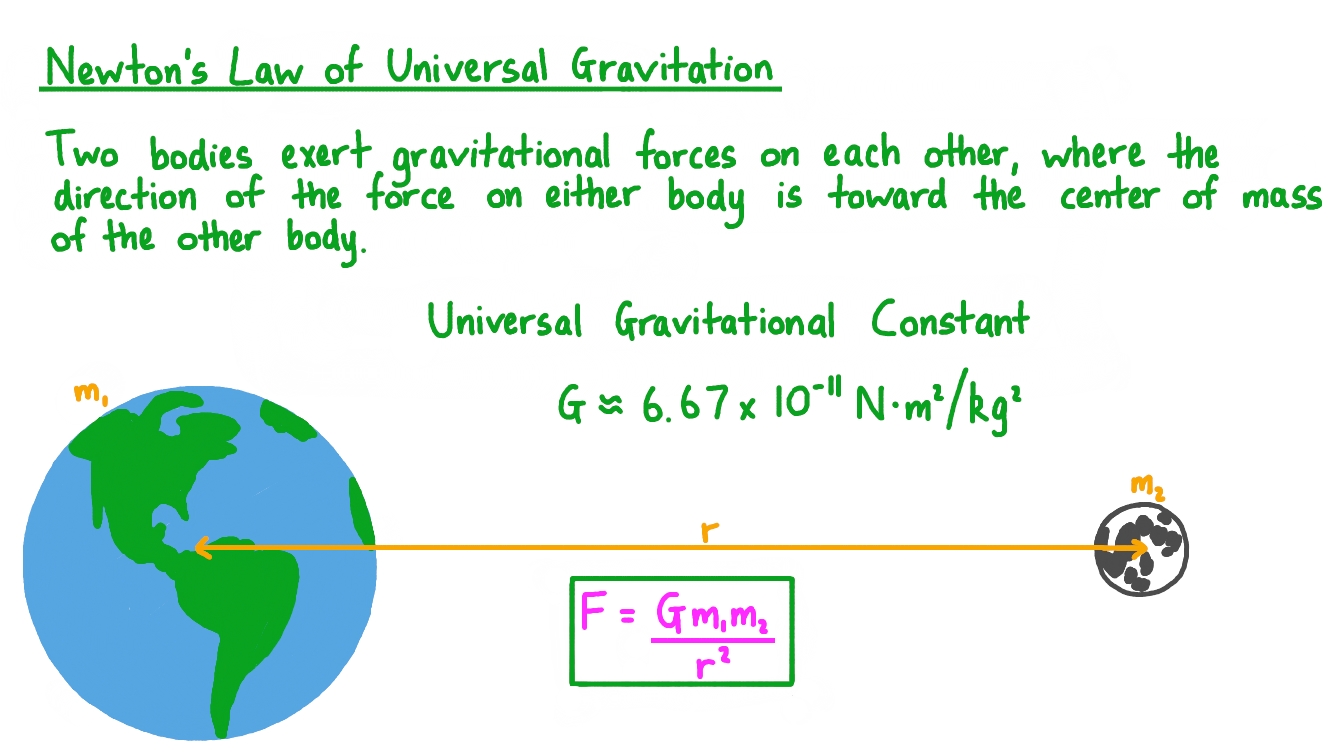
State the universal law of
gravitation.
The Universal Law of Gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This means the force of attraction is stronger with larger masses and weaker with greater distances.
Mathematical Representation:
The force (F) of gravity between two objects is described by the equation:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Where:
G is the universal gravitational constant (approximately 6.67 x 10⁻¹¹ Nm²/kg²).
m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects.
r is the distance between the centers of the two objects.
Key points:
The force is always attractive.
The force acts along the line connecting the centers of the two objects.
The value of G is the same throughout the universe, making it a universal constant.