What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Autotrophic Nutrition:
Self-Sustaining:
Autotrophs don’t rely on other organisms for food.
Primary Producers:
They form the base of food chains, converting inorganic substances into organic matter.
Examples:
Photosynthesis: Green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Chemosynthesis: Certain bacteria use chemical energy from inorganic compounds to produce food.
Necessary Conditions:
Access to inorganic substances (e.g., carbon dioxide, water).
A source of energy (light or chemicals).
Heterotrophic Nutrition:
Dependent: Heterotrophs rely on other organisms or organic matter for sustenance.
Consumers: They obtain energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms.
Examples:
Herbivores: Animals that eat plants.
Carnivores: Animals that eat other animals.
Omnivores: Animals that eat both plants and animals.
Decomposers: Organisms that break down dead organic matter.
Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition:
Chemoheterotrophy: Obtaining energy from the oxidation of organic compounds (most animals, fungi, and bacteria).
Photoheterotrophy: Using light as an energy source and organic compounds as a carbon source (some bacteria).
In essence, autotrophs are producers, making their own food, while heterotrophs are consumers, relying on other organisms for food.
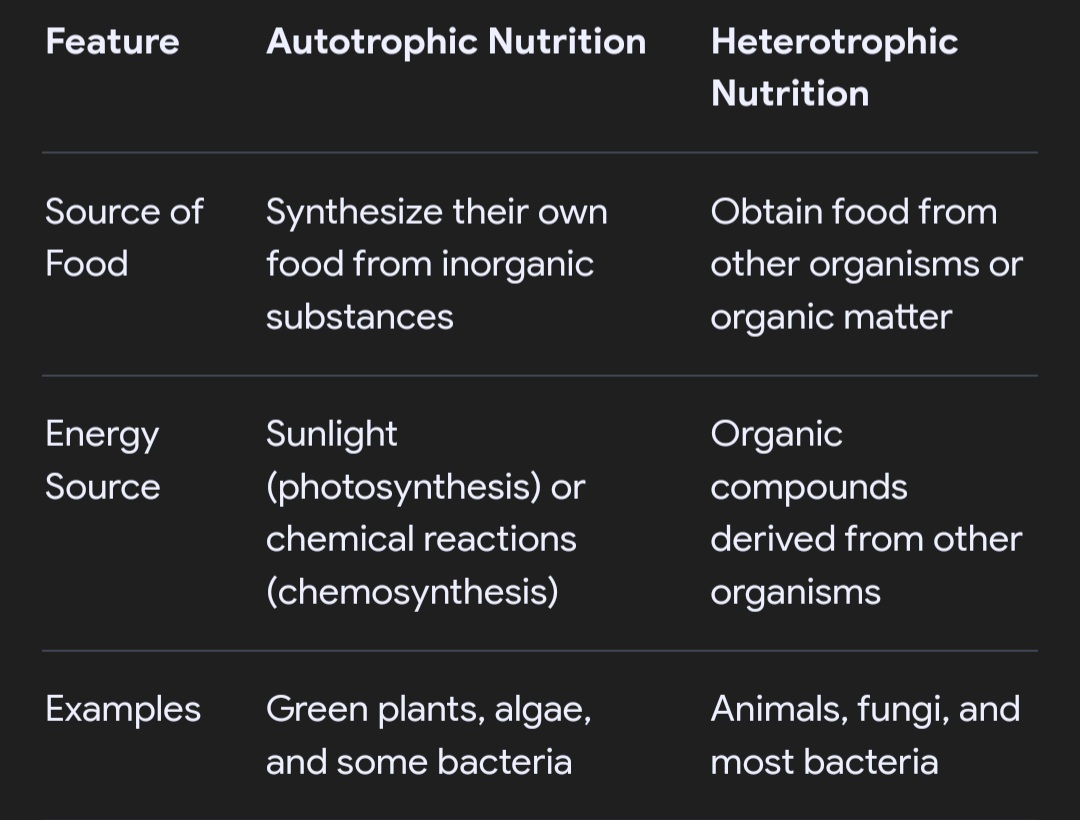
Autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition are two primary modes of nutrition in organisms. Autotrophs make their own food from inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water, often using sunlight (photosynthesis) or chemical energy (chemosynthesis). Heterotrophs, on the other hand, obtain their food by consuming other organisms or organic matter, relying on pre-existing organic compounds.
Autotrophic nutrition involves organisms making their own food from inorganic substances, like plants using photosynthesis, while heterotrophic nutrition involves organisms consuming other organisms for food. Autotrophs are “self-feeders” producing their own food from non-living sources, like sunlight or chemicals, while heterotrophs are “other-feeders” consuming other organisms for sustenance.
Key Differences:
Source of Food:
Autotrophs produce their food from inorganic sources (like CO2, water, and sunlight), whereas heterotrophs obtain their food from other organisms or organic matter.
Energy Source:
Autotrophs primarily use light energy (photosynthesis) or chemical energy (chemosynthesis) to create their food, while heterotrophs obtain energy by breaking down the organic matter they consume.
Examples:
Autotrophs include plants, algae, and some bacteria, while heterotrophs include animals, fungi, and many other bacteria.
Position in Food Chain:
Autotrophs are producers, forming the base of food chains, while heterotrophs are consumers, feeding on other organisms.