How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
In human beings, oxygen is transported via the blood, primarily bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells, and also partially dissolved in plasma. Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, is transported from tissues to the lungs primarily dissolved in the plasma, and a small amount is carried bound to hemoglobin.
Oxygen Transport:
1. Absorption:
Oxygen is absorbed from the air in the lungs into the bloodstream through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
2. Hemoglobin Binding:
As oxygen enters the bloodstream, it primarily binds to hemoglobin molecules within red blood cells (RBCs). This forms oxyhemoglobin, where oxygen is carried throughout the body.
3. Delivery to Tissues:
Oxygenated blood, containing oxyhemoglobin, is pumped by the heart and distributed to all tissues and organs.
4. Diffusion to Cells:
As the blood circulates through capillaries, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the surrounding cells where it is needed for cellular respiration.
Carbon Dioxide Transport:
1. Production and Dissolution:
Carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product of cellular respiration and diffuses from the cells into the bloodstream.
2. Plasma Transport:
A significant portion of carbon dioxide dissolves directly into the blood plasma and is transported in this dissolved form.
3. Hemoglobin and Bicarbonate:
Some carbon dioxide binds to hemoglobin, forming carbaminohemoglobin, and a larger portion is converted into bicarbonate ions within the red blood cells.
4. Transport to Lungs:
The carbon dioxide, in its various forms, is transported back to the lungs where it is released into the alveoli during exhalation.
5. Exhalation:
The carbon dioxide is then exhaled from the body through the lungs.
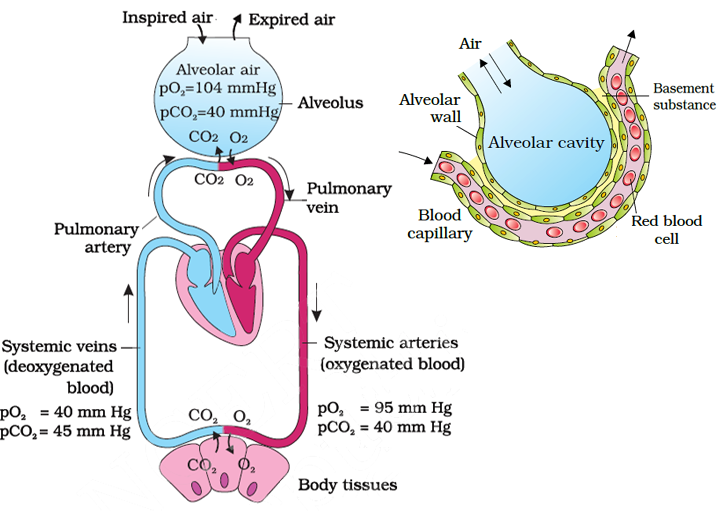
Blood is the medium of transport for O2
and CO2
. About 97 per cent of O2
is
transported by RBCs in the blood. The remaining 3 per cent of O2
is carried
in a dissolved state through the plasma. Nearly 20-25 per cent of CO2
is
transported by RBCs whereas 70 per cent of it is carried as bicarbonate.
About 7 per cent of CO2
is carried in a dissolved state through plasma.
14.4.1 Transport of Oxygen
Haemoglobin is a red coloured iron containing pigment present in the
RBCs. O2
can bind with haemoglobin in a reversible manner to form
oxyhaemoglobin. Each haemoglobin molecule can carry a maximum of
four molecules of O2
. Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is primarily
related to partial pressure of O2
. Partial pressure of CO2
, hydrogen ion
concentration and temperature are the other factors which can interfere
with this binding. A sigmoid curve is obtained when percentage saturation
of haemoglobin with O2
is plotted against the
pO2
. This curve is called the Oxygen
dissociation curve (Figure 14.5) and is highly
useful in studying the effect of factors like
pCO2
, H+
concentration, etc., on binding of O2
with haemoglobin. In the alveoli, where there
is high pO2
, low pCO2
, lesser H+
concentration
and lower temperature, the factors are
all favourable for the formation of
oxyhaemoglobin, whereas in the tissues,
where low pO2
, high pCO2
, high H+
concentration and higher temperature exist,
the conditions are favourable for dissociation
of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin. This
clearly indicates that O2
gets bound to
haemoglobin in the lung surface and gets
dissociated at the tissues. Every 100 ml of
oxygenated blood can deliver around 5 ml of
O2
to the tissues under normal physiological
conditions.
14.4.2 Transport of Carbon dioxide
CO2
is carried by haemoglobin as carbamino-haemoglobin (about
20-25 per cent). This binding is related to the partial pressure of CO2
.
pO2
is a major factor which could affect this binding. When pCO2
is high
and pO2
is low as in the tissues, more binding of carbon dioxide occurs
whereas, when the pCO2
is low and pO2
is high as in the alveoli, dissociation BIOLOGY
of CO2
from carbamino-haemoglobin takes place, i.e., CO2
which is bound
to haemoglobin from the tissues is delivered at the alveoli. RBCs contain
a very high concentration of the enzyme, carbonic anhydrase and minute
quantities of the same is present in the plasma too. This enzyme facilitates
the following reaction in both directions.
CO H O H CO
Carbonic
anhydrase
Carbonic
anhydra
2 2 + ← → 2 3
se
← → HCO H+
− +
3
At the tissue site where partial pressure of CO2
is high due to
catabolism, CO2
diffuses into blood (RBCs and plasma) and forms HCO3
–
and H+,. At the alveolar site where pCO2
is low, the reaction proceeds in
the opposite direction leading to the formation of CO2
and H2O. Thus,
CO2
trapped as bicarbonate at the tissue level and transported to the
alveoli is released out as CO2 (Figure 14.4). Every 100 ml of deoxygenated
blood delivers approximately 4 ml of CO2
to the alveoli.
In human beings, oxygen is primarily transported from the lungs to tissues by hemoglobin in red blood cells, while carbon dioxide is mostly transported back to the lungs in a dissolved form within the blood plasma.
Oxygen Transport:
In the lungs: Oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the bloodstream.
Binding to hemoglobin: Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, binds to oxygen, forming oxyhemoglobin.
Circulation: The blood, now oxygenated, is circulated throughout the body by the heart.
Tissue delivery: At the tissues, oxygen diffuses out of the blood and into the cells for cellular respiration.
Deoxygenated blood: The blood, now depleted of oxygen, returns to the lungs via the circulatory system.
Carbon Dioxide Transport:
1. Production in tissues:
Carbon dioxide is produced as a byproduct of cellular respiration in the body’s tissues.
2. Dissolved in blood:
A significant portion of carbon dioxide dissolves directly into the blood plasma.
3. Bicarbonate formation:
Some carbon dioxide reacts with water in the blood to form bicarbonate ions, which are also transported back to the lungs.
4. Lung exchange:
In the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood and into the alveoli.
5. Exhalation:
Carbon dioxide is then exhaled from the body.